swin transformer中相对位置编码解析
Published:
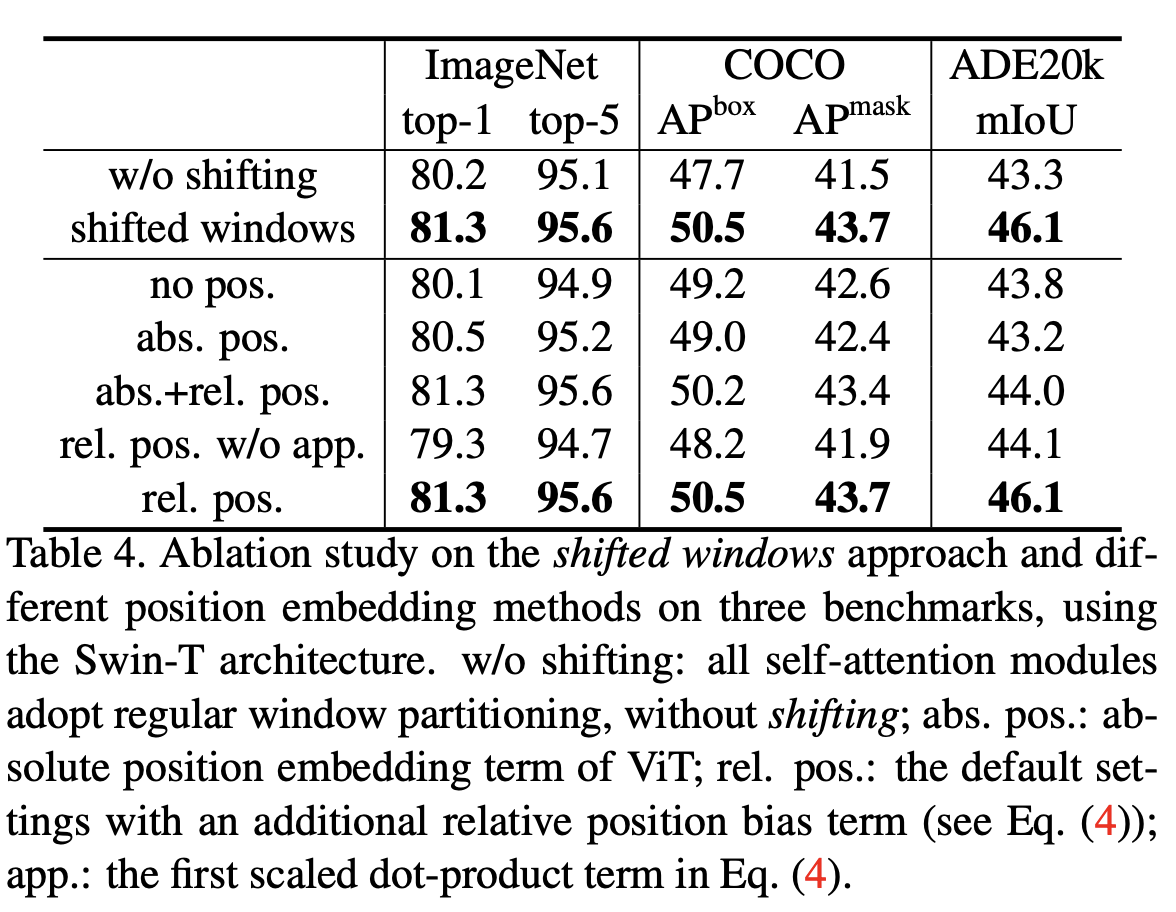
在论文中,作者发现相对位置编码的效果会更好一些。 
代码的实现为:
# get pair-wise relative position index for each token inside the window
coords_h = torch.arange(self.window_size[0])
coords_w = torch.arange(self.window_size[1])
coords = torch.stack(torch.meshgrid([coords_h, coords_w])) # 2, Wh, Ww
coords_flatten = torch.flatten(coords, 1) # 2, Wh*Ww
relative_coords = coords_flatten[:, :, None] - coords_flatten[:, None, :] # 2, Wh*Ww, Wh*Ww
relative_coords = relative_coords.permute(1, 2, 0).contiguous() # Wh*Ww, Wh*Ww, 2
relative_coords[:, :, 0] += self.window_size[0] - 1 # shift to start from 0
relative_coords[:, :, 1] += self.window_size[1] - 1
relative_coords[:, :, 0] *= 2 * self.window_size[1] - 1
relative_position_index = relative_coords.sum(-1) # Wh*Ww, Wh*Ww
self.register_buffer("relative_position_index", relative_position_index)
在forward中的计算为:
relative_position_bias = self.relative_position_bias_table[self.relative_position_index.view(-1)].view(
self.window_size[0] * self.window_size[1], self.window_size[0] * self.window_size[1], -1) # Wh*Ww,Wh*Ww,nH
relative_position_bias = relative_position_bias.permute(2, 0, 1).contiguous() # nH, Wh*Ww, Wh*Ww
attn = attn + relative_position_bias.unsqueeze(0)
完整的class实现为:
class WindowAttention(nn.Module):
r""" Window based multi-head self attention (W-MSA) module with relative position bias.
It supports both of shifted and non-shifted window.
Args:
dim (int): Number of input channels.
window_size (tuple[int]): The height and width of the window.
num_heads (int): Number of attention heads.
qkv_bias (bool, optional): If True, add a learnable bias to query, key, value. Default: True
qk_scale (float | None, optional): Override default qk scale of head_dim ** -0.5 if set
attn_drop (float, optional): Dropout ratio of attention weight. Default: 0.0
proj_drop (float, optional): Dropout ratio of output. Default: 0.0
"""
def __init__(self, dim, window_size, num_heads, qkv_bias=True, qk_scale=None, attn_drop=0., proj_drop=0.):
super().__init__()
self.dim = dim
self.window_size = window_size # Wh, Ww
self.num_heads = num_heads
head_dim = dim // num_heads
self.scale = qk_scale or head_dim ** -0.5
# define a parameter table of relative position bias
self.relative_position_bias_table = nn.Parameter(
torch.zeros((2 * window_size[0] - 1) * (2 * window_size[1] - 1), num_heads)) # 2*Wh-1 * 2*Ww-1, nH
# get pair-wise relative position index for each token inside the window
coords_h = torch.arange(self.window_size[0])
coords_w = torch.arange(self.window_size[1])
coords = torch.stack(torch.meshgrid([coords_h, coords_w])) # 2, Wh, Ww
coords_flatten = torch.flatten(coords, 1) # 2, Wh*Ww
relative_coords = coords_flatten[:, :, None] - coords_flatten[:, None, :] # 2, Wh*Ww, Wh*Ww
relative_coords = relative_coords.permute(1, 2, 0).contiguous() # Wh*Ww, Wh*Ww, 2
relative_coords[:, :, 0] += self.window_size[0] - 1 # shift to start from 0
relative_coords[:, :, 1] += self.window_size[1] - 1
relative_coords[:, :, 0] *= 2 * self.window_size[1] - 1
relative_position_index = relative_coords.sum(-1) # Wh*Ww, Wh*Ww
self.register_buffer("relative_position_index", relative_position_index)
self.qkv = nn.Linear(dim, dim * 3, bias=qkv_bias)
self.attn_drop = nn.Dropout(attn_drop)
self.proj = nn.Linear(dim, dim)
self.proj_drop = nn.Dropout(proj_drop)
trunc_normal_(self.relative_position_bias_table, std=.02)
self.softmax = nn.Softmax(dim=-1)
def forward(self, x, mask=None):
"""
Args:
x: input features with shape of (num_windows*B, N, C)
mask: (0/-inf) mask with shape of (num_windows, Wh*Ww, Wh*Ww) or None
"""
B_, N, C = x.shape
qkv = self.qkv(x).reshape(B_, N, 3, self.num_heads, C // self.num_heads).permute(2, 0, 3, 1, 4)
q, k, v = qkv[0], qkv[1], qkv[2] # make torchscript happy (cannot use tensor as tuple)
q = q * self.scale
attn = (q @ k.transpose(-2, -1))
relative_position_bias = self.relative_position_bias_table[self.relative_position_index.view(-1)].view(
self.window_size[0] * self.window_size[1], self.window_size[0] * self.window_size[1], -1) # Wh*Ww,Wh*Ww,nH
relative_position_bias = relative_position_bias.permute(2, 0, 1).contiguous() # nH, Wh*Ww, Wh*Ww
attn = attn + relative_position_bias.unsqueeze(0)
if mask is not None:
nW = mask.shape[0]
attn = attn.view(B_ // nW, nW, self.num_heads, N, N) + mask.unsqueeze(1).unsqueeze(0)
attn = attn.view(-1, self.num_heads, N, N)
attn = self.softmax(attn)
else:
attn = self.softmax(attn)
attn = self.attn_drop(attn)
x = (attn @ v).transpose(1, 2).reshape(B_, N, C)
x = self.proj(x)
x = self.proj_drop(x)
return x
def extra_repr(self) -> str:
return f'dim={self.dim}, window_size={self.window_size}, num_heads={self.num_heads}'
def flops(self, N):
# calculate flops for 1 window with token length of N
flops = 0
# qkv = self.qkv(x)
flops += N * self.dim * 3 * self.dim
# attn = (q @ k.transpose(-2, -1))
flops += self.num_heads * N * (self.dim // self.num_heads) * N
# x = (attn @ v)
flops += self.num_heads * N * N * (self.dim // self.num_heads)
# x = self.proj(x)
flops += N * self.dim * self.dim
return flops
| 这个计算过程,我们用windows size = 2为例来看一下计算过程。图片取自链接[transformer入门 论文阅读(4) Swin Transformer | shifted window,relative position bias详解](https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/507105020) |
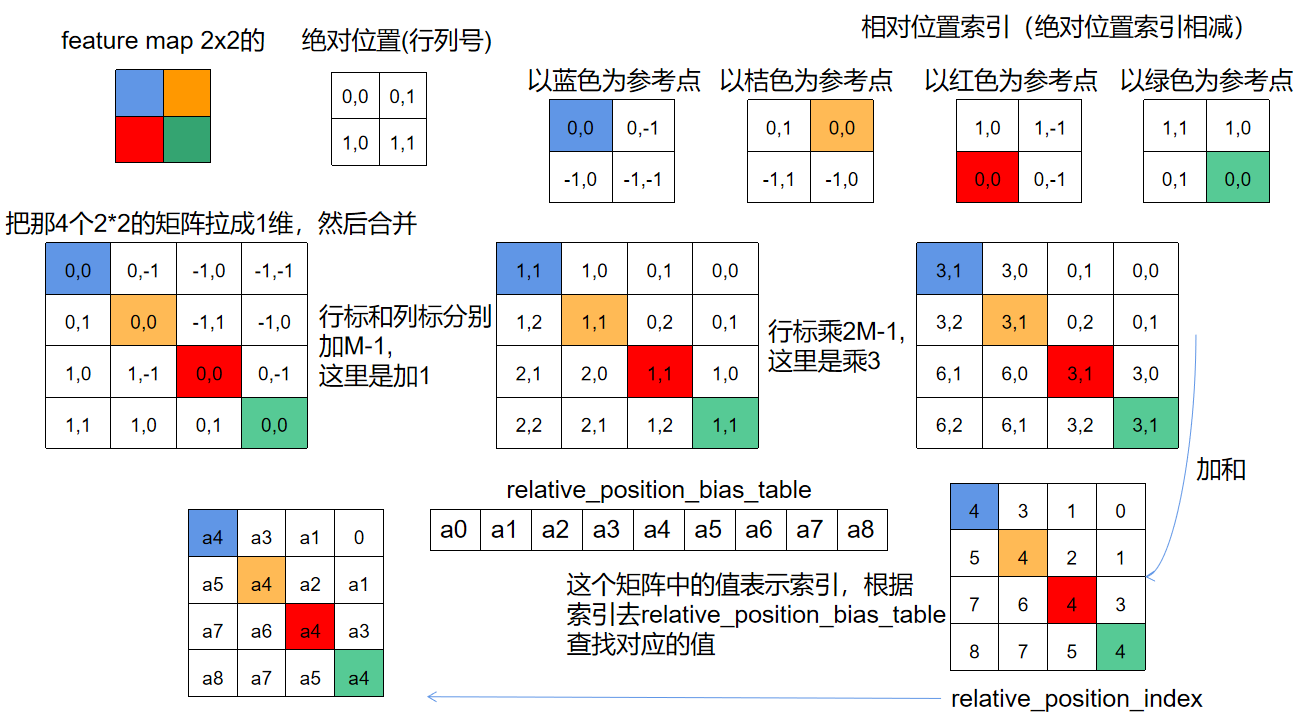
通过这个图示,是比较容易理解相对位置编码的计算过程的,下面我们在实际的代码上跑一下,看看实际的数值变化,以及在forward中的计算过程。
我们使用swin transformer的imagenet image classification任务为例,逐步来解释每行代码。在这个任务中,window_size = 7。
1. 定义relative_position_bias_table
# define a parameter table of relative position bias
self.relative_position_bias_table = nn.Parameter(
torch.zeros((2 * window_size[0] - 1) * (2 * window_size[1] - 1), num_heads)) # 2*Wh-1 * 2*Ww-1, nH
这个定义了relative_position_bias_table,对应上图示中的relative_position_bias_table。
这个值的初始化值为shape为[169, 4]的全0值。169是(2 * window_size[0] - 1) * (2 * window_size[1] - 1),也就是(27-1)(2*7-1) = 169.
然后将其初始化为一个服从截断正态分布的随机值,标准差为 0.02。截断正态分布的范围通常限制在均值两侧一定范围内,避免生成过大或过小的值。
trunc_normal_(self.relative_position_bias_table, std=.02)
经过截断和正态分布的初始化后,self.relative_position_bias_table的shape是[169, 4],说明有169个相对位置可以索引,有4个头。
self.relative_position_bias_table的值是:
self.relative_position_bias_table = Parameter containing:
tensor([[ 1.3016e-02, 1.2930e-02, 1.5971e-02, -2.9950e-02],
[-1.2150e-02, -1.8186e-02, 1.8201e-02, -2.9683e-02],
[-1.4085e-03, -9.6917e-03, 1.7187e-02, -2.1197e-02],
[ 4.5870e-04, -2.5759e-02, 1.0428e-02, 7.8378e-03],
...
[-4.6959e-03, -1.1017e-02, 1.3361e-02, 7.7851e-03],
[ 1.7211e-02, -9.5882e-03, 6.2699e-02, 7.8999e-03],
[ 1.5927e-02, -5.5237e-02, 1.6605e-02, -1.4664e-02],
[-2.6448e-02, 8.7442e-03, 5.1785e-03, 3.0192e-02]],
requires_grad=True)
这个shape的原因是:
相对位置的意义为:对于窗口注意力机制,每个 token 的位置都是相对于窗口内其他 token 定义的。窗口大小为 (Wh, Ww),窗口内总共有 Wh * Ww 个 token。相对位置表示的是两个 token 在垂直方向(高度)和水平方向(宽度)上的偏移量。
例如:
- 一个窗口大小为
(3, 3):- 水平相对位置范围是:
[-2, -1, 0, 1, 2](总共2 * Wh - 1 = 5)。 - 垂直相对位置范围是:
[-2, -1, 0, 1, 2](总共2 * Ww - 1 = 5)。
- 水平相对位置范围是:
这意味着在 2D 平面中,窗口内的 token 之间的相对位置总共有:
(2 * Wh - 1) * (2 * Ww - 1)
例如,(3, 3) 窗口有 5 * 5 = 25 种可能的相对位置。
self.relative_position_bias_table` 的形状是(2 * window_size[0] - 1) * (2 * window_size[1] - 1), num_heads)
- 第一维度:
(2 * Wh - 1) * (2 * Ww - 1),表示所有可能的相对位置。 - 第二维度:
num_heads,因为每个注意力头都会有一个单独的偏置。
例如:
- 窗口大小
(3, 3),有25种可能的相对位置,num_heads=8。 - 则
relative_position_bias_table的形状为(25, 8)。
这一表将存储每个相对位置对于每个注意力头的偏置值。
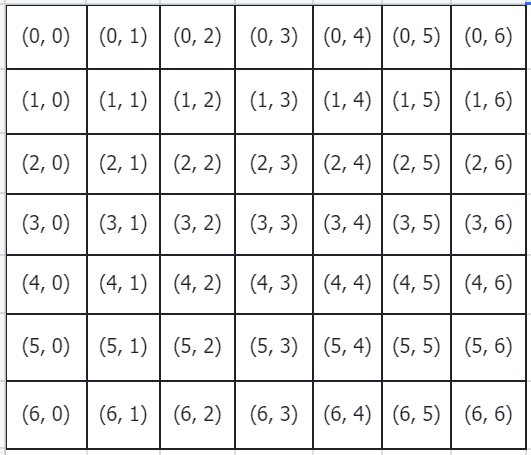
2.获取绝对位置
# get pair-wise relative position index for each token inside the window
coords_h = torch.arange(self.window_size[0])
coords_w = torch.arange(self.window_size[1])
coords = torch.stack(torch.meshgrid([coords_h, coords_w])) # 2, Wh, Ww
coords_flatten = torch.flatten(coords, 1) # 2, Wh*Ww
在这里,
coords_h = tensor([0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6]), coords_w = tensor([0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6])
经过meshgrid和stack计算之后,
coords = tensor([[[0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
[1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1],
[2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2],
[3, 3, 3, 3, 3, 3, 3],
[4, 4, 4, 4, 4, 4, 4],
[5, 5, 5, 5, 5, 5, 5],
[6, 6, 6, 6, 6, 6, 6]],
[[0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6],
[0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6],
[0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6],
[0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6],
[0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6],
[0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6],
[0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6]]])
用图示表示就是
然后经过flatten计算
coords_flatten = tensor(
[[0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 3, 3, 3,3, 3, 3, 3, 4, 4, 4, 4, 4, 4, 4, 5, 5, 5, 5, 5, 5, 5, 6, 6, 6, 6, 6, 6,6],
[0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 0, 1, 2,3, 4, 5, 6, 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6]])
coords_flatten.shape = torch.Size([2, 49])
展平后代表的是相同的意义,只是排列形式发生了变化。
3.获取相对位置索引(通过绝对位置相减)
relative_coords = coords_flatten[:, :, None] - coords_flatten[:, None, :] # 2, Wh*Ww, Wh*Ww
relative_coords = relative_coords.permute(1, 2, 0).contiguous() # Wh*Ww, Wh*Ww, 2
coords_flatten[:, :, None]是shape为[2, 49, 1]的tensor。None在最后添加了一维。
coords_flatten[:, :, None] = tensor([[[0],
[0],
[0],
[0],
[0],
[0],
[0],
[1],
[1],
[1],
[1],
[1],
[1],
[1],
[2],
[2],
[2],
[2],
[2],
[2],
[2],
[3],
[3],
[3],
[3],
[3],
[3],
[3],
[4],
[4],
[4],
[4],
[4],
[4],
[4],
[5],
[5],
[5],
[5],
[5],
[5],
[5],
[6],
[6],
[6],
[6],
[6],
[6],
[6]],
[[0],
[1],
[2],
[3],
[4],
[5],
[6],
[0],
[1],
[2],
[3],
[4],
[5],
[6],
[0],
[1],
[2],
[3],
[4],
[5],
[6],
[0],
[1],
[2],
[3],
[4],
[5],
[6],
[0],
[1],
[2],
[3],
[4],
[5],
[6],
[0],
[1],
[2],
[3],
[4],
[5],
[6],
[0],
[1],
[2],
[3],
[4],
[5],
[6]]])
coords_flatten[:, None, :]是shape为[2, 1, 49]的tensor,None在中间添加了一维。
coords_flatten[:, None, :] = tensor(
[[[0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 3, 3,3, 3, 3, 3, 3, 4, 4, 4, 4, 4, 4, 4, 5, 5, 5, 5, 5, 5, 5, 6, 6, 6, 6,6, 6, 6]],
[[0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 0, 1,2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 0, 1, 2, 3,4, 5, 6]]])
coords_flatten[:, None, :]与coords_flatten在数值上是一致的,只是多添加了一维。
coords_flatten = tensor(
[[0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 3, 3, 3,3, 3, 3, 3, 4, 4, 4, 4, 4, 4, 4, 5, 5, 5, 5, 5, 5, 5, 6, 6, 6, 6, 6, 6,6],
[0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 0, 1, 2,3, 4, 5, 6, 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6]])
coords_flatten[:, :, None]的shape是[2, 49, 1],coords_flatten[:, None, :]的shape是[2, 1, 49],通过广播机制进行相减,得到相对坐标relative_coords,relative_coords = coords_flatten[:, :, None] - coords_flatten[:, None, :]。
relative_coords =
tensor([[[ 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -2, -2, -2,
-2, -2, -2, -2, -3, -3, -3, -3, -3, -3, -3, -4, -4, -4, -4, -4, -4,
-4, -5, -5, -5, -5, -5, -5, -5, -6, -6, -6, -6, -6, -6, -6],
[ 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -2, -2, -2,
-2, -2, -2, -2, -3, -3, -3, -3, -3, -3, -3, -4, -4, -4, -4, -4, -4,
-4, -5, -5, -5, -5, -5, -5, -5, -6, -6, -6, -6, -6, -6, -6],
[ 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -2, -2, -2,
-2, -2, -2, -2, -3, -3, -3, -3, -3, -3, -3, -4, -4, -4, -4, -4, -4,
-4, -5, -5, -5, -5, -5, -5, -5, -6, -6, -6, -6, -6, -6, -6],
[ 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -2, -2, -2,
-2, -2, -2, -2, -3, -3, -3, -3, -3, -3, -3, -4, -4, -4, -4, -4, -4,
-4, -5, -5, -5, -5, -5, -5, -5, -6, -6, -6, -6, -6, -6, -6],
...
4, 4, 4, 4, 3, 3, 3, 3, 3, 3, 3, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2,
2, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
[ 6, 6, 6, 6, 6, 6, 6, 5, 5, 5, 5, 5, 5, 5, 4, 4, 4,
4, 4, 4, 4, 3, 3, 3, 3, 3, 3, 3, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2,
2, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0]],
[[ 0, -1, -2, -3, -4, -5, -6, 0, -1, -2, -3, -4, -5, -6, 0, -1, -2,
-3, -4, -5, -6, 0, -1, -2, -3, -4, -5, -6, 0, -1, -2, -3, -4, -5,
-6, 0, -1, -2, -3, -4, -5, -6, 0, -1, -2, -3, -4, -5, -6],
[ 1, 0, -1, -2, -3, -4, -5, 1, 0, -1, -2, -3, -4, -5, 1, 0, -1,
-2, -3, -4, -5, 1, 0, -1, -2, -3, -4, -5, 1, 0, -1, -2, -3, -4,
...
[ 5, 4, 3, 2, 1, 0, -1, 5, 4, 3, 2, 1, 0, -1, 5, 4, 3,
2, 1, 0, -1, 5, 4, 3, 2, 1, 0, -1, 5, 4, 3, 2, 1, 0,
-1, 5, 4, 3, 2, 1, 0, -1, 5, 4, 3, 2, 1, 0, -1],
[ 6, 5, 4, 3, 2, 1, 0, 6, 5, 4, 3, 2, 1, 0, 6, 5, 4,
3, 2, 1, 0, 6, 5, 4, 3, 2, 1, 0, 6, 5, 4, 3, 2, 1,
0, 6, 5, 4, 3, 2, 1, 0, 6, 5, 4, 3, 2, 1, 0]]])
relative_coords的shape是torch.Size([2, 49, 49])。
针对relative_coords的第[2,0,49]的数值,用图示所示就是下图所示,以蓝色点为参考点,其他点相对参考点的距离。
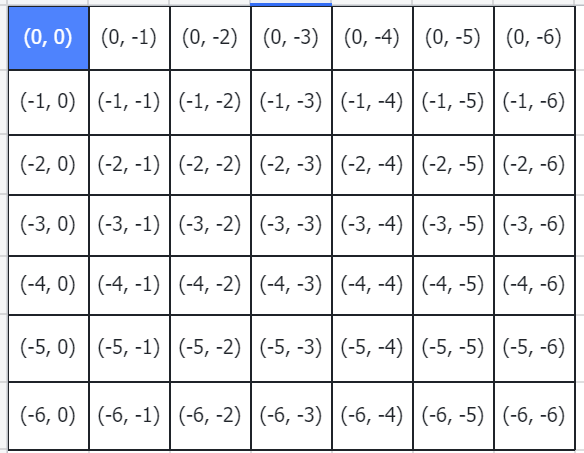
然后以黄色点为参考点,其他点相对参考点的距离。
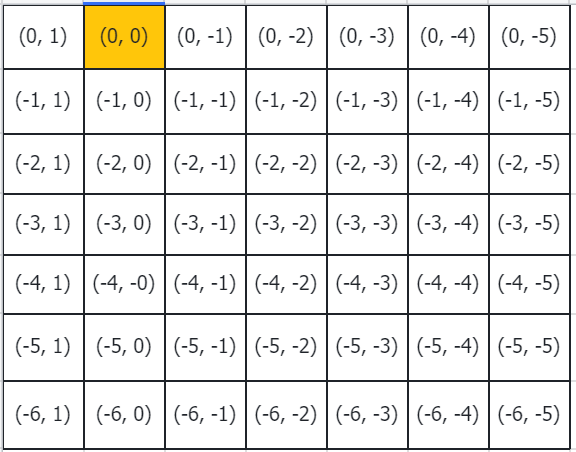
剩下的依次类推。
整体就是知乎文章图中这部分 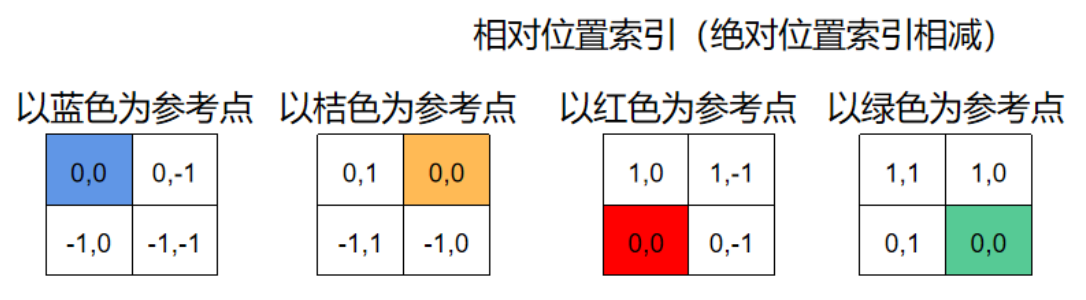 的扩展。
的扩展。
4. 将shape为[2,49,49]relative_coords的49个不同参考点的相对距离值拉成一维
relative_coords = relative_coords.permute(1, 2, 0).contiguous() # Wh*Ww, Wh*Ww, 2
此操作对应示例中的 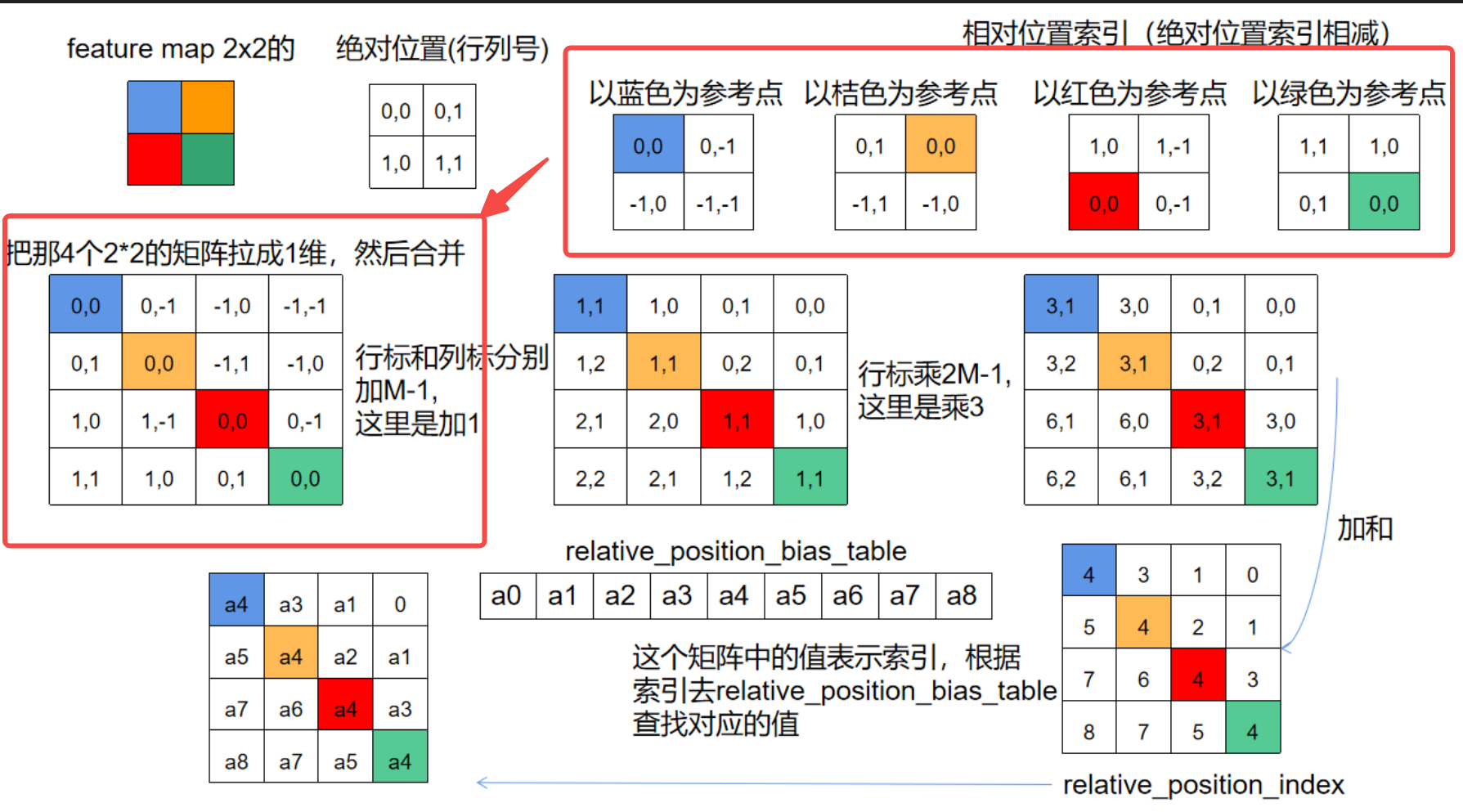
经过处理后,relative_coords的shape是[49, 49, 2]。他的值可以用下面的图示表示: 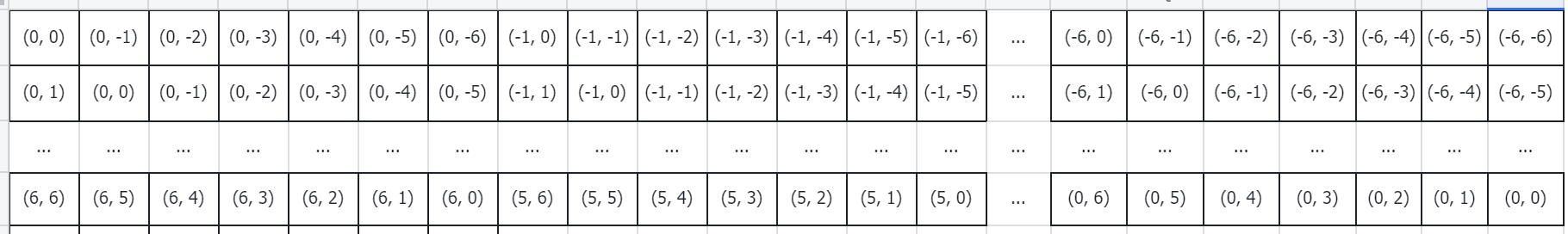
即将以每一个参考点来说,其他位置的点的相对距离,都放在一行上。relative_coords的值是:
tensor([[[ 0, 0],
[ 0, -1],
[ 0, -2],
[ 0, -3],
[ 0, -4],
[ 0, -5],
[ 0, -6],
[-1, 0],
[-1, -1],
[-1, -2],
[-1, -3],
[-1, -4],
[-1, -5],
[-1, -6],
[-2, 0],
[-2, -1],
[-2, -2],
[-2, -3],
[-2, -4],
[-2, -5],
[-2, -6],
[-3, 0],
[-3, -1],
[-3, -2],
[-3, -3],
[-3, -4],
[-3, -5],
[-3, -6],
[-4, 0],
[-4, -1],
[-4, -2],
[-4, -3],
[-4, -4],
[-4, -5],
[-4, -6],
[-5, 0],
[-5, -1],
[-5, -2],
[-5, -3],
[-5, -4],
[-5, -5],
[-5, -6],
[-6, 0],
[-6, -1],
[-6, -2],
[-6, -3],
[-6, -4],
[-6, -5],
[-6, -6]],
[[ 0, 1],
[ 0, 0],
...
[ 0, 1],
[ 0, 0],
[ 0, -1]],
[[ 6, 6],
[ 6, 5],
[ 6, 4],
[ 6, 3],
[ 6, 2],
[ 6, 1],
[ 6, 0],
[ 5, 6],
[ 5, 5],
[ 5, 4],
[ 5, 3],
[ 5, 2],
[ 5, 1],
[ 5, 0],
[ 4, 6],
[ 4, 5],
[ 4, 4],
[ 4, 3],
[ 4, 2],
[ 4, 1],
[ 4, 0],
[ 3, 6],
[ 3, 5],
[ 3, 4],
[ 3, 3],
[ 3, 2],
[ 3, 1],
[ 3, 0],
[ 2, 6],
[ 2, 5],
[ 2, 4],
[ 2, 3],
[ 2, 2],
[ 2, 1],
[ 2, 0],
[ 1, 6],
[ 1, 5],
[ 1, 4],
[ 1, 3],
[ 1, 2],
[ 1, 1],
[ 1, 0],
[ 0, 6],
[ 0, 5],
[ 0, 4],
[ 0, 3],
[ 0, 2],
[ 0, 1],
[ 0, 0]]])
5.对横纵坐标值进行数值处理
relative_coords[:, :, 0] += self.window_size[0] - 1 # shift to start from 0
relative_coords[:, :, 1] += self.window_size[1] - 1
relative_coords[:, :, 0] *= 2 * self.window_size[1] - 1
relative_coords[:, :, 0]代表的是所有的横坐标,relative_coords[:, :, 1]代表的是所有的纵坐标。
relative_coords[:, :, 0]和relative_coords[:, :, 1]的shape都是[49, 49]。
relative_coords[:, :, 0] =
tensor([[ 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -2, -2, -2, -2,
-2, -2, -2, -3, -3, -3, -3, -3, -3, -3, -4, -4, -4, -4, -4, -4, -4, -5,
-5, -5, -5, -5, -5, -5, -6, -6, -6, -6, -6, -6, -6],
[ 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -2, -2, -2, -2,
-2, -2, -2, -3, -3, -3, -3, -3, -3, -3, -4, -4, -4, -4, -4, -4, -4, -5,
-5, -5, -5, -5, -5, -5, -6, -6, -6, -6, -6, -6, -6],
...
[ 6, 6, 6, 6, 6, 6, 6, 5, 5, 5, 5, 5, 5, 5, 4, 4, 4, 4,
4, 4, 4, 3, 3, 3, 3, 3, 3, 3, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 1,
1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
[ 6, 6, 6, 6, 6, 6, 6, 5, 5, 5, 5, 5, 5, 5, 4, 4, 4, 4,
4, 4, 4, 3, 3, 3, 3, 3, 3, 3, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 1,
1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
[ 6, 6, 6, 6, 6, 6, 6, 5, 5, 5, 5, 5, 5, 5, 4, 4, 4, 4,
4, 4, 4, 3, 3, 3, 3, 3, 3, 3, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 1,
1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0]])
relative_coords[:, :, 1] =
tensor([[ 0, -1, -2, -3, -4, -5, -6, 0, -1, -2, -3, -4, -5, -6, 0, -1, -2, -3,
-4, -5, -6, 0, -1, -2, -3, -4, -5, -6, 0, -1, -2, -3, -4, -5, -6, 0,
-1, -2, -3, -4, -5, -6, 0, -1, -2, -3, -4, -5, -6],
[ 1, 0, -1, -2, -3, -4, -5, 1, 0, -1, -2, -3, -4, -5, 1, 0, -1, -2,
-3, -4, -5, 1, 0, -1, -2, -3, -4, -5, 1, 0, -1, -2, -3, -4, -5, 1,
0, -1, -2, -3, -4, -5, 1, 0, -1, -2, -3, -4, -5],
[ 2, 1, 0, -1, -2, -3, -4, 2, 1, 0, -1, -2, -3, -4, 2, 1, 0, -1,
-2, -3, -4, 2, 1, 0, -1, -2, -3, -4, 2, 1, 0, -1, -2, -3, -4, 2,
1, 0, -1, -2, -3, -4, 2, 1, 0, -1, -2, -3, -4],
...
[ 5, 4, 3, 2, 1, 0, -1, 5, 4, 3, 2, 1, 0, -1, 5, 4, 3, 2,
1, 0, -1, 5, 4, 3, 2, 1, 0, -1, 5, 4, 3, 2, 1, 0, -1, 5,
4, 3, 2, 1, 0, -1, 5, 4, 3, 2, 1, 0, -1],
[ 6, 5, 4, 3, 2, 1, 0, 6, 5, 4, 3, 2, 1, 0, 6, 5, 4, 3,
2, 1, 0, 6, 5, 4, 3, 2, 1, 0, 6, 5, 4, 3, 2, 1, 0, 6,
5, 4, 3, 2, 1, 0, 6, 5, 4, 3, 2, 1, 0]])
第一步是横纵坐标都加6,避免距离值是负值。
relative_coords[:, :, 0] += self.window_size[0] - 1 # shift to start from 0
relative_coords[:, :, 1] += self.window_size[1] - 1
经过计算后,relative_coords变成:
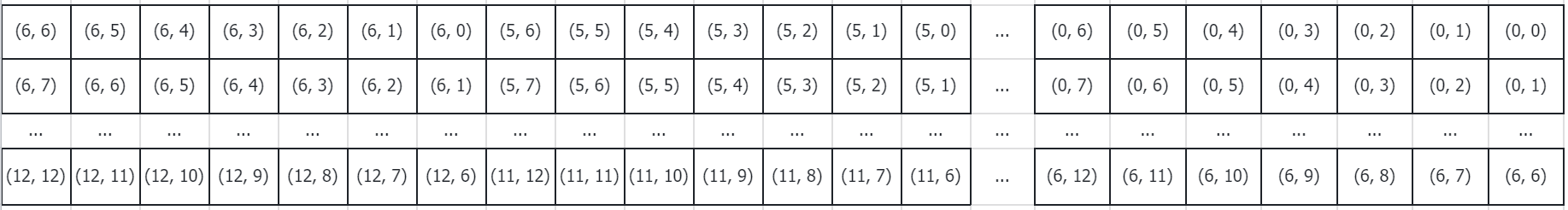
然后对横坐标乘以2 * self.window_size[1] - 1。
relative_coords[:, :, 0] *= 2 * self.window_size[1] - 1
经过计算后,relative_coords的值为
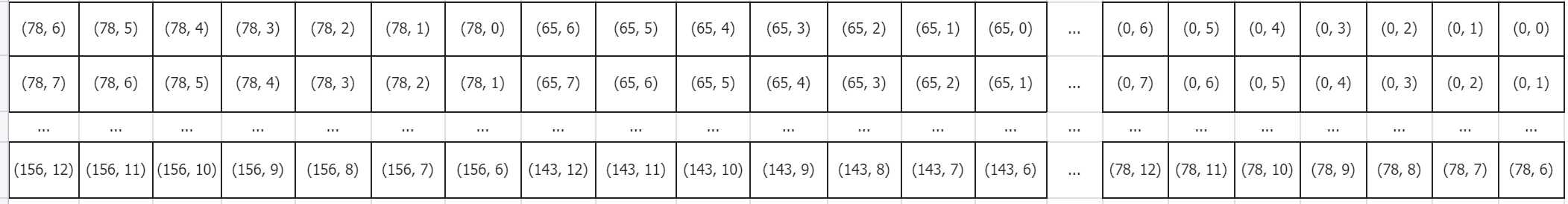
对横坐标乘以2 * self.window_size[1] - 1后,这里面的最大值为左下角的(156,12),156+12=168. 我们在最开始定义的relative_position_bias_table的shape也是(169, num_heads) 的,正好可以把relative_position_bias_table全部索引到。
# define a parameter table of relative position bias
self.relative_position_bias_table = nn.Parameter(
torch.zeros((2 * window_size[0] - 1) * (2 * window_size[1] - 1), num_heads)) # 2*Wh-1 * 2*Ww-1, nH
6. 横纵坐标加和
relative_position_index = relative_coords.sum(-1) # Wh*Ww, Wh*Ww
relative_position_index =
tensor([[ 84, 83, 82, 81, 80, 79, 78, 71, 70, 69, 68, 67, 66, 65,
58, 57, 56, 55, 54, 53, 52, 45, 44, 43, 42, 41, 40, 39,
32, 31, 30, 29, 28, 27, 26, 19, 18, 17, 16, 15, 14, 13,
6, 5, 4, 3, 2, 1, 0],
[ 85, 84, 83, 82, 81, 80, 79, 72, 71, 70, 69, 68, 67, 66,
59, 58, 57, 56, 55, 54, 53, 46, 45, 44, 43, 42, 41, 40,
33, 32, 31, 30, 29, 28, 27, 20, 19, 18, 17, 16, 15, 14,
7, 6, 5, 4, 3, 2, 1],
...
[167, 166, 165, 164, 163, 162, 161, 154, 153, 152, 151, 150, 149, 148,
141, 140, 139, 138, 137, 136, 135, 128, 127, 126, 125, 124, 123, 122,
115, 114, 113, 112, 111, 110, 109, 102, 101, 100, 99, 98, 97, 96,
89, 88, 87, 86, 85, 84, 83],
[168, 167, 166, 165, 164, 163, 162, 155, 154, 153, 152, 151, 150, 149,
142, 141, 140, 139, 138, 137, 136, 129, 128, 127, 126, 125, 124, 123,
116, 115, 114, 113, 112, 111, 110, 103, 102, 101, 100, 99, 98, 97,
90, 89, 88, 87, 86, 85, 84]])
relative_position_index的shape是[49, 49]。这里面最大的值是168,最小的值是0,正好可以对最开始的self.relative_position_bias_table的值全部索引到,self.relative_position_bias_table的shape是[169,4],169个可索引的位置,4个头。
7. forward中的计算
relative_position_bias = self.relative_position_bias_table[self.relative_position_index.view(-1)].view(
self.window_size[0] * self.window_size[1], self.window_size[0] * self.window_size[1], -1) # Wh*Ww,Wh*Ww,nH
relative_position_bias = relative_position_bias.permute(2, 0, 1).contiguous() # nH, Wh*Ww, Wh*Ww
attn = attn + relative_position_bias.unsqueeze(0)
将其拆分来看。我们把上面的代码拆分为:
relative_position_index_tmp = self.relative_position_index.view(-1)
relative_position_bias_table_tmp = self.relative_position_bias_table[relative_position_index_tmp]
relative_position_bias = relative_position_bias_table_tmp.view(
self.window_size[0] * self.window_size[1], self.window_size[0] * self.window_size[1], -1) # Wh*Ww,Wh*Ww,nH
relative_position_bias = relative_position_bias.permute(2, 0, 1).contiguous() # nH, Wh*Ww, Wh*Ww
attn = attn + relative_position_bias.unsqueeze(0)
- self.relative_position_index.view(-1)操作
上面已经说到relative_position_index的shape是[49, 49],view(-1)操作会将所有的值放在一个维度,所以假设relative_position_index_tmp = self.relative_position_index.view(-1),relative_position_index_tmp的shape是[2401],relative_position_index_tmp的值是
tensor([ 84, 83, 82, 81, 80, 79, 78, 71, 70, 69, 68, 67, 66, 65,
58, 57, 56, 55, 54, 53, 52, 45, 44, 43, 42, 41, 40, 39,
32, 31, 30, 29, 28, 27, 26, 19, 18, 17, 16, 15, 14, 13,
6, 5, 4, 3, 2, 1, 0, 85, 84, 83, 82, 81, 80, 79,
72, 71, 70, 69, 68, 67, 66, 59, 58, 57, 56, 55, 54, 53,
46, 45, 44, 43, 42, 41, 40, 33, 32, 31, 30, 29, 28, 27,
20, 19, 18, 17, 16, 15, 14, 7, 6, 5, 4, 3, 2, 1,
86, 85, 84, 83, 82, 81, 80, 73, 72, 71, 70, 69, 68, 67,
60, 59, 58, 57, 56, 55, 54, 47, 46, 45, 44, 43, 42, 41,
...
128, 127, 126, 125, 124, 123, 122, 115, 114, 113, 112, 111, 110, 109,
102, 101, 100, 99, 98, 97, 96, 89, 88, 87, 86, 85, 84, 83,
168, 167, 166, 165, 164, 163, 162, 155, 154, 153, 152, 151, 150, 149,
142, 141, 140, 139, 138, 137, 136, 129, 128, 127, 126, 125, 124, 123,
116, 115, 114, 113, 112, 111, 110, 103, 102, 101, 100, 99, 98, 97,
90, 89, 88, 87, 86, 85, 84], device='cuda:0')
- self.relative_position_bias_table[relative_position_index_tmp]操作
上面说到,self.relative_position_bias_table的shape是[169,4],在上面也有打印它的值。relative_position_index_tmp的shape是[2401]的索引值,所以此步操作就相当于对self.relative_position_bias_table做2401次索引,每次索引出来的都是shape为[1,4]的tensor,所以 relative_position_bias_table_tmp = self.relative_position_bias_table[relative_position_index_tmp]后,relative_position_bias_table_tmp的shape为[2401, 4],他的部分值展示如下:
tensor([[-2.7874e-02, -3.6342e-02, 2.8827e-02, -2.3673e-02],
[ 4.1464e-02, 7.6075e-03, 5.3314e-03, -1.4585e-03],
[-1.4711e-02, -1.3424e-02, -1.3756e-03, -1.3826e-03],
[-3.6255e-02, -1.9680e-03, 1.6092e-02, 2.3690e-02],
...
[-2.0880e-02, -1.2093e-02, 4.1462e-02, 1.8901e-02],
[-1.6958e-02, -6.0754e-03, -1.3342e-02, -7.5932e-04],
[ 8.9761e-03, -1.1548e-02, -2.5437e-02, 1.5095e-02],
[-2.7874e-02, -3.6342e-02, 2.8827e-02, -2.3673e-02]]
- relative_position_bias_table_tmp.view(self.window_size[0] * self.window_size[1],self.window_size[0] * self.window_size[1], -1)操作
这一步就是将之前的view(-1)操作再转换回原始尺寸。所以relative_position_bias = relative_position_bias_table_tmp.view(self.window_size[0] * self.window_size[1], self.window_size[0] * self.window_size[1], -1),relative_position_bias的shape是[49, 49, 4].
- relative_position_bias.permute(2, 0, 1).contiguous()操作
上一步relative_position_bias的shape是[49, 49, 4],经过permute操作后,shape变为[4, 49, 49].
attn = attn + relative_position_bias.unsqueeze(0),attn经过attention计算后,shape是([6400, 4, 49, 49]),这里的relative_position_bias经过unsqueeze一下,正好可以和attn的结果相加。
